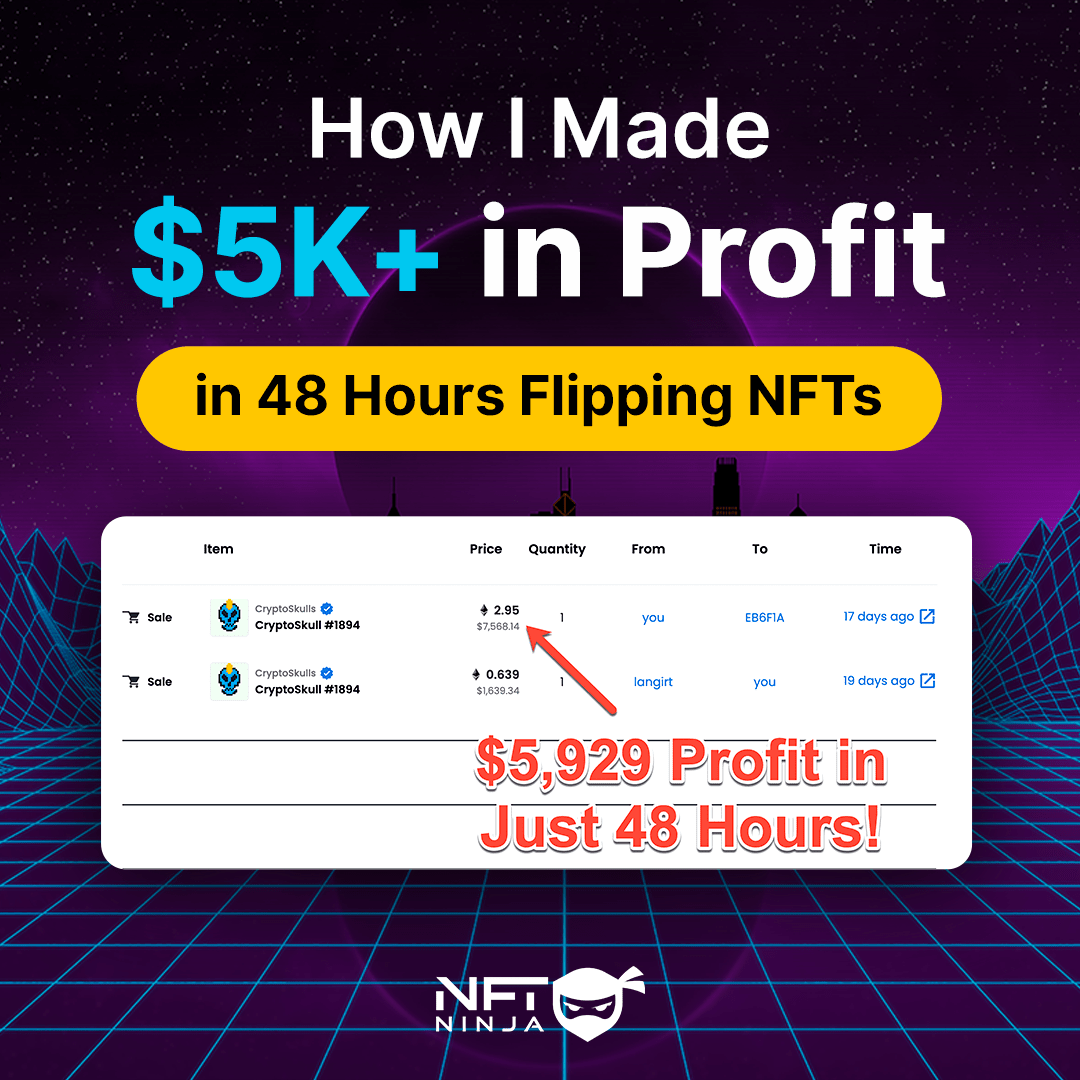
As Bitcoin’s mining difficulty exceeds 80 trillion, anticipation mounts for the upcoming halving event, expected to further impact the network’s dynamics.
Steady Rise in Mining Difficulty
Bitcoin’s mining difficulty, a measure of the challenge in adding new blocks to the blockchain, has surged past 80 trillion. With the network’s hash rate reaching 562.81 exahashes per second, this marks a record high for mining difficulty, up from 81.73 trillion, as reported by BTC.com. The trend of increasing difficulty has been consistent since January 2023, with projections hinting at a climb to 100 trillion in the near future.
Impact of Mining Difficulty
Higher mining difficulty signifies greater computational power and energy required by miners to validate transactions and secure the network. As difficulty levels soar, miners face intensified competition, driving up operational costs. The anticipated 6% increase in mining difficulty signals ongoing challenges for miners, pushing the metric to unprecedented heights.
Bitcoin’s Halving Event
The upcoming Bitcoin halving, slated for late April, will see mining rewards reduced by half, from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC. Historically, halving events are integral to Bitcoin’s supply dynamics, occurring roughly every four years to combat inflation. As rewards diminish, less efficient miners may struggle to sustain operations, potentially leading to a decline in hash rate post-halving.
Potential Impact on Network Dynamics
Galaxy’s mining analysts suggest that up to 20% of Bitcoin’s current hash rate could go offline following the halving. This shift could favor more efficient mining rigs, reshaping the network’s composition and influencing mining difficulty. A reduced hash rate could prompt a subsequent adjustment in difficulty, reflecting the network’s efforts to maintain a consistent block production rate.
Conclusion
Bitcoin’s surging mining difficulty underscores the evolving landscape of blockchain operations, with anticipation building ahead of the upcoming halving event. As miners navigate heightened competition and operational challenges, the network’s resilience and adaptability will be tested amidst changing dynamics.